Biomarkers
Companion Diagnostics | Disease Progression | Therapeutic Success
GenXPro GmbH is a pioneer in advanced biomarker discovery, specializing in ultra-sensitive detection and analysis of cell-free nucleic acids. From small RNA and miRNA to cfRNA, cfDNA methylation patterns, and cfDNA mutations, GenXPro’s technologies support highly accurate liquid biopsy analyses for a broad range of research and clinical applications.
Biomarkers based on cfRNA, cfDNA & methylation
We are profiling mRNA, smallRNA (microRNA), non-coding RNA, DNA, methylation of the DNA (epigenetics) and examine specific characteristics of them for high-resolution biomarker identification. Based on the findings, qPCR- or other single- or multigene assays are developed for cost-efficient biomarker analyses.
Precision in Small RNA, miRNA, and cfRNA Analysis
GenXPro’s TrueQuant technology eliminates PCR-induced bias and captures small RNA species — including miRNAs, piRNAs, and other non-coding RNAs — with unmatched sensitivity. Even minute inputs, such as a few microliters of plasma, can be profiled with single-tube protocols that preserve rare biomarker signatures, making GenXPro’s smallRNA and cfRNA workflows ideal for non-invasive liquid biopsy testing.
Our proven expertise in these highly sensitive workflows has enabled successful biomarker discovery across a broad spectrum of diseases, including cancer, neurodegenerative disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. Researchers and clinicians trust GenXPro’s solutions to reveal novel biomarkers that support early detection, improve prognostic accuracy, and guide personalized treatment decisions. By delivering robust data from precious and limited specimens, GenXPro empowers breakthrough research that is shaping the future of diagnostics and precision medicine.
Cutting-Edge cfDNA Methylation and Mutation Analyses
Beyond RNA, GenXPro offers comprehensive cfDNA solutions. Our expertise extends to methylation analysis — a powerful biomarker for cancer and other diseases — enabling genome-wide mapping of epigenetic signatures to detect early-stage cancers or monitor therapy response.
In addition, GenXPro’s high-sensitivity cfDNA mutation detection assays pinpoint single-nucleotide variants and other genomic alterations with robust error-correction strategies, even from ultra-low DNA inputs. These advanced techniques make GenXPro’s cfDNA portfolio ideal for early diagnosis, relapse monitoring, and personalized medicine.
Integrated Multi-Omics for Personalized Health
With its focus on both cfDNA and cfRNA, we provide a holistic molecular profile for every sample. This multi-omic integration — combining epigenetic, genetic, and transcriptomic signatures — empowers the discovery of novel biomarkers and an may support the development of highly personalized therapies.
Additionally, our experienced bioinformatics team guides data analysis and interpretation, delivering actionable results that drive progress in diagnostics, drug discovery, and precision oncology.
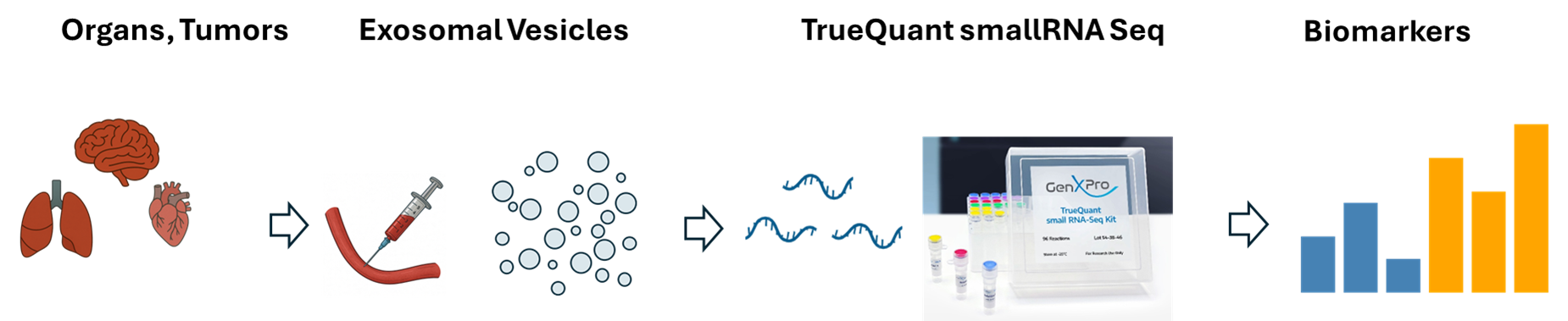
Extracellular / Exosomal Vesicles – EVs
Extracellular vesicles (EVs), including exosomes, are rich carriers of RNA and DNA that can be profiled from plasma, urine, saliva, and even aqueous humor. Extending our TrueQuant smallRNA-Seq, panRNA-Seq, and cfDNA (methylation & mutation) capabilities, we offer EV isolation, nucleic-acid extraction, and end-to-end NGS workflows optimized for ultra-low volumes and rare biomarker detection—seamlessly aligned with the RNA and cfDNA strengths already described on this page.
- EV-RNA: miRNAs, piRNAs, tRNA fragments, lncRNAs, and circRNAs via TrueQuant smallRNA-Seq or panRNA-Seq with UMI-based bias control and single-tube prep (ideal for precious samples).
- EV-cfDNA: methylation (bisulfite or enzymatic) and somatic mutations (SNVs/indels/CNVs) with high sensitivity on low-input libraries (UMIs + dual indices).
- Multi-omics from the same EV fraction: combine transcriptomic and epigenetic signatures for discovery and panel design.
Use cases: non-invasive biomarker discovery in oncology, cardiovascular and neurodegeneration research; longitudinal monitoring; early detection studies and companion-diagnostics development.
Aqueous Humor–derived Analyses (Ocular Liquid Biopsy)
For ophthalmic conditions where tissue biopsy is risky or infeasible, we support robust NGS from ≤100 µL of aqueous humor (AH).
Our workflows enable TrueQuant smallRNA-Seq, panRNA-Seq (small + long RNAs in a single assay), and cfDNA methylation/mutation profiling—extending the liquid-biopsy solutions you already use for plasma or urine to ocular fluids.

What we analyze from AH
- Small RNAs / miRNAs (single-sample, non-pooled AH feasible by NGS).
- Total RNA (panRNA-Seq): joint detection of small and long RNA classes for broader discovery.
- cfDNA methylation & mutations: UMI-based error suppression for low-input AH cfDNA, aligned with our cfDNA portfolio. :contentReference
Typical study designs
- AH-only or AH + matched plasma/saliva/urine to compare ocular vs. systemic signatures.
- Discovery → targeted validation (qPCR/panels) under our bioinformatics guidance.
- Longitudinal sampling for therapy monitoring or relapse assessment.
Selected Aqueous Humor publications
- Machine learning-based identification of small RNA signatures in aqueous humor as a step toward precision diagnosis of glaucoma — Dobrzycka M., Sulewska A., Konopińska J., et al., Annals of Medicine, 2025 (open-access PDF). AH small-RNA signatures with ML for glaucoma stratification.
- A proteotranscriptomic approach to dissect the molecular landscape of human retinoblastoma — Wolf J., Hajdu R.I., Boneva S., et al., Frontiers in Oncology, 2025 — discusses AH liquid biopsy in the context of retinoblastoma and multi-omics.
- Detection of microRNAs expression signatures in vitreous humor of intraocular tuberculosis — Chadalawada S., Rathinam S.R., Lalitha P., et al., Molecular Biology Reports, 2023 — complementary vitreous-humor miRNA signatures relevant to ocular TB.
- Dysregulated expression of microRNAs in aqueous humor from intraocular tuberculosis patients — Chadalawada S., Kathirvel K., Lalitha P., et al., Molecular Biology Reports, 2022. Identifies 56 AH miRNAs with validation of key markers and pathway involvement in IOTB.
- Dysregulated Expression of microRNAs in Aqueous Humor from Intraocular Tuberculosis Patients — Devarajan B., Chadalawada S., et al., IOVS abstract, 2020. Shows AH miRNA dysregulation as potential IOTB markers; inputs typically 50–100 µL
- MicroRNA profiling in aqueous humor of individual human eyes by next-generation sequencing — Wecker T., Hoffmeier K., Plötner A., et al., Investigative Ophthalmology & Visual Science, 2016. Demonstrates feasibility of miRNome NGS from individual AH samples and discusses plasma/ocular contributions.
Note: The same ultra-sensitive principles described above for smallRNA/cfRNA and cfDNA methylation/mutations apply to AH with our low-input, single-tube, UMI-enabled workflows.